Ancient Roman Empires: The ancient city of Rome was established at around 8th century BC. It grew from various settlements around the river Tiber.

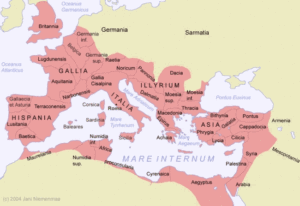
The Roman Empire was an autocratic form of government ruling over the regions around the Mediterranean and centered at Rome. It was one of the largest civilizations of the world and contributed greatly to government, law, war, art, literature, etc.
Ancient Roman Empires
The Roman civilization went through three phases. In the beginning, it was a monarchy and was ruled by kings. This continued till seven kings ruled Rome. At around 509 BC, the seventh and last king of Rome, Tarquin the Proud, was deposed, and a republic was formed by the people of Rome.
They established a system of annually elected magistrates and various representative assemblies. They set up a council known as the ‘senate’ which ruled over the city of Rome. The most important authorities were the two consuls appointed by the Senate, who exercised both executive and military authority.
Roman Empires Facts
The consuls were appointed for only a year. There were two levels of voting, the Comitia Centuriata (centuriate assembly), which voted for important offices and matters like wars, etc and the comitia Tribute (tribal assembly), which elected for less important offices. This republic led to successful governance of Rome and lasted until 23 BC that is for around 500 years.
Slowly, even this very successful Roman Republic also came to an end. The main reason was the many civil wars that happened, which weakened the republic. Gradually, the republic turned into a very autocratic Roman Empire.
Roman empire timeline
The three main events that mark the transition from republic to empire are Julius Caesar’s appointment as a dictator at around 44BC, the Battle of Actium on 2nd September, 31 BC and the granting of the honorific title of Augustus to Octavian by the Roman Senate on 4th January, 27 BC.
Thus Augustus assumed absolute power and became the first emperor of Rome, retaining only the pretense of the republican system of government. This also happened to be the glorious period of the Roman civilization.
Augustus was followed by many able emperors like Tiberius, who was the successor of Augustus, the ‘five good emperors’ namely, Nerva, Trajan, Hadrian, Antoninus Pius, and Marcus Aurelius, and several others. The empire of Rome was said to be at its territorial, cultural and economic peak under these rulers.
Then came what is now known as the ‘Crisis of Third Century’. Between the period of 193 and 235 BC, there came many incompetent rulers. Combining that with the increasing power of the army led to a long period of imperial collapse and external invasions.
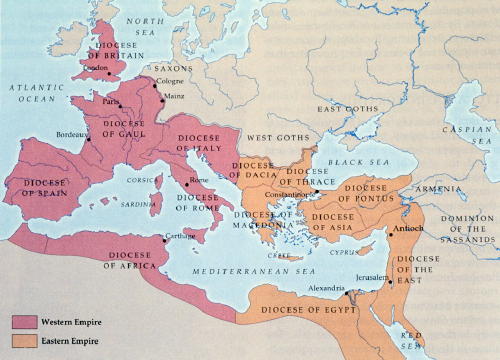
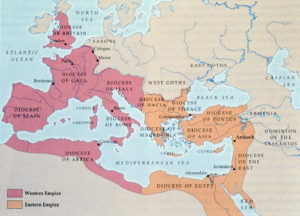
This was put to an end by a very competent ruler, Diocletian, who introduced the practice of dividing the authority between four co-emperors. Slowly, this led to the division of the empire along the east-west axis.
On 11th May, 330 BC Emperor Constantine established Byzantium as his capital, renaming it Constantinople, thus permanently dividing the Empire of Rome into Western Roman Empire and Eastern Roman Empire.
Western Roman Empire
The Western Roman Empire was eventually overrun by huge migrations from eastern and northern Europe. Such huge migrations posed a too great a difficulty for the Romans to stem thus leading to a gradual decline of the Western Roman Empire over the centuries. Finally in 410 BC, the Visigoths under the leadership of Alaric I captured Rome.
Eastern Roman Empire
The Eastern Roman Empire, which later came to be known as the Byzantine Empire, survived for almost 900 years and became one of the most flourishing and stable Christian Empire.

Eventually, Byzantine was threatened by the followers of Islam who had conquered the areas of Syria, Armenia, and Egypt during the Byzantine Arab wars. Finally, the Byzantine Empire collapsed in !493 after the death of Constantine XI and the capture of Constantinople by the Ottoman Turks led by Mehmed-II.